
What can be done if a Patient Procedure does not fall into the available bundle of coded services?
Code bundling can be beneficial in many instances but there is potential for issues to occur when a patient requires a service that doesn’t fall into a set of codes that can be bundled. This can put a provider at risk for not being reimbursed for the additional services.
In this situation, there is also unfortunately the potential for a healthcare provider to avoid performing a particular service or procedure, or to bill the patient more than they should, in order to ensure they receive full payment for all procedures provided. This tactic of over-billing is referred to as upcoding, and is an illegal medical practice.
The practice of “Bundling” is considered useful and logical for payers to put similar services and package them as one when it comes to a financial standpoint. However, there could be circumstances when there is a need to bill for an additional service that doesn’t belong to that specific ‘package’ or ‘bundle’ of codes.
In this situation, unfortunately there are limited options: a) Providers leave out the additional service(s) performed entirely and lose revenue. b) They bill while upcoding the services which also can be considered as over-billing and illegal. c) Billers may get a denial from the payer that says: “These procedures cannot be billed together, since they are mutually exclusive”. Which is a hassle in itself to manage.
So, what can be done?
National Correct Coding Initiative Edits:
The whole concept of bundling and unbundling comes from something called NCCI edits. More specifically Procedure to Procedure (PTP) Edits. Unbundling can be performed via specific modifier(s) indicators described in the columns of NCCI edits. Which basically tells what can be unbundled or not.
NCCI edits documents are released by CMS every year and easily available on their website. It should look something like this:
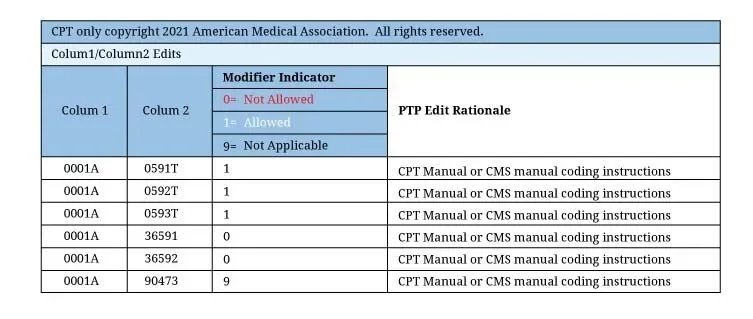
Within NCCI’s correct coding edits, unbundling is permitted when the codes are assigned a “1” indicator (provided requirements are met and reported with the appropriate modifier), but never when they are assigned a “0” indicator.
What Modifiers can be used to Unbundle Procedures from one another?
Modifier are two-digits codes, used in claims to provide additional information along with service performed.
Let’s have a look at list of modifiers that be used to unbundle procedures. When appended carefully and rightfully they might just improve the chances for the claims to be reimbursed in various scenarios
Modifier 25:
Very commonly used Modifier to unbundle E/M visits from other services performed on the same day. This modifier is only to be used with E/M services.
Modifier 24:
This Modifier will allow you to separate services rendered during a global surgery period of 10 or 90 days.
Modifier 59 and its subsets:
Also, the most popular modifier used to unbundle similar procedures performed on the same day. Modifier 59 is notoriously abused to by-pass NCCI bundling edits and should only be used where it is properly justified. That’s why CMS created its subsets which are quite self-explanatory:
- XE Separate Encounter, A Service That Is Distinct Because It Occurred During A Separate Encounter
- XS Separate Structure, A Service That Is Distinct Because It Was Performed On A Separate Organ/Structure
- XP Separate Practitioner, A Service That Is Distinct Because It Was Performed By A Different Practitioner
- XU Unusual Non-Overlapping Service, The Use Of A Service That Is Distinct Because It Does Not Overlap Usual Components Of The Main Service
Modifier 51:
Modifier 51 is used on the second and subsequent operative procedure(s) performed by the same physician on the same day. Modifier 51 may also be used when multiple procedures coded in the Medicine chapter of CPT (medical procedures) are performed at the same session or when surgical and medical procedures are performed together.
Modifier 91:
Modifier 91 is used exclusively to report any repeated clinical diagnostic laboratory test(s) being billed if a single service (same CPT code) is ordered for the same beneficiary on the same day of service. The repeated laboratory test should be medically necessary.
Final Word
When billing similar or mutually exclusive procedures it can be very helpful to have a look at the NCCI edits and the modifier indicators. Being familiar with these modifiers can be extremely helpful to get the additional services reimbursed that were performed rightfully and also escape the unwanted denials that come with it. Also, it is to keep in mind unbundling should always be done when there is enough medical evidence to back it up before you go ahead and append those modifiers!
For more information you may contact any of our Medical Billing Experts.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter!
Enter Your Email Address. We Promise We Won't Spam You
